Prompt engineering is no longer just a clever trick for better answers. In 2025, it is a fundamental part of any serious AI system
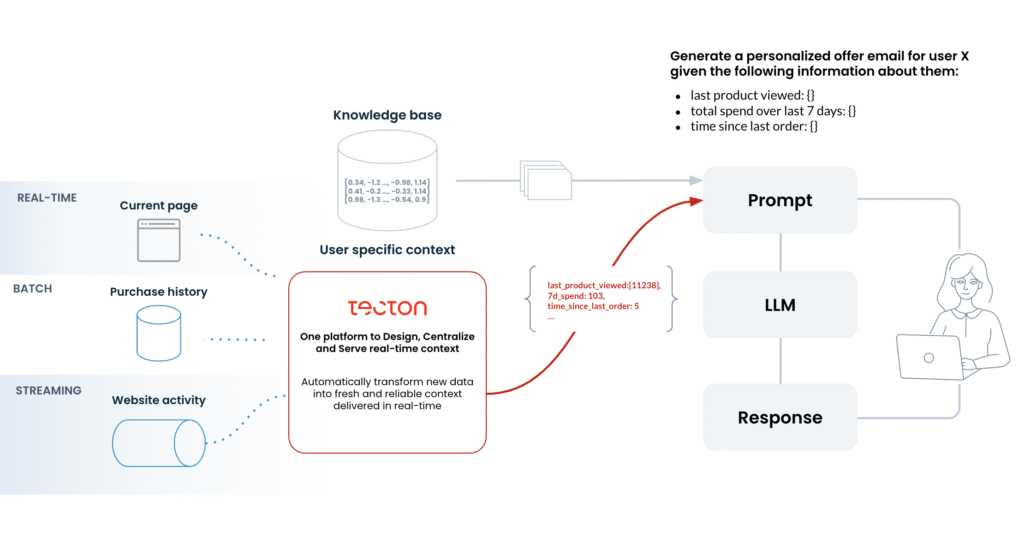
Whether you are building an assistant, automating documents, or handling user queries, prompt design now directly affects the system’s reliability, speed, safety, and usability.
Let’s explore how prompt engineering fits into real-world systems and why it matters.
6.1 Prompting is System Behavior
A prompt does more than send instructions to a model. It defines how the model behaves. Specifically, it outlines what the model should do, which information to use, how to structure its response, and which boundaries it must respect.
In traditional software, developers use code to control behavior. In contrast, generative systems rely on prompts, memory, and context. Therefore, even with a highly capable model, the entire system can fail if the prompt is unclear or poorly written.
To learn more about how LLMs interpret inputs, see:
→ OpenAI’s guide to prompt engineering
→ Anthropic’s Claude prompt guide
6.2 Design Prompts Like Interfaces
Just like a user interface, a good prompt gives clear and useful guidance. It helps the model understand what to do and how to respond.
Before writing a prompt, consider the following questions:
- What is the model’s role in this task
- What input does it need to do its job
- What should the output look like
- How do you define success or failure
- What should happen if the request is unsafe or ambiguous
By answering these, you treat the prompt as part of the system’s design, not just a last-minute instruction.
This approach is similar to how teams design user experiences. For a deeper dive, explore:
→ The Prompt Engineering Guide
→ Building LLM UX Patterns (Github)
6.3 Patterns from Real Applications
Across tools like chatbots, copilots, and research assistants, several design patterns appear consistently. These patterns help ensure the model produces useful, safe, and predictable responses.
| Situation | Prompt design pattern |
|---|---|
| Output must be consistent | Use anchoring and formatting |
| Task involves reasoning | Use scaffolding and step-by-step logic |
| Context is long or complex | Use structured prompts with context windows |
| Input might be unsafe | Add filters and fallback instructions |
| Prompts are reused at scale | Track versions and test with examples |
In each case, strong prompt engineering involves:
- A clear and repeatable structure
- A strategy for handling unclear or harmful inputs
- A testing process to confirm the output is accurate
You can explore practical examples of these patterns in action with:
→ Smol Developer Agents Course
→ Prompt Engineering Best Practices (Brev.dev)
6.4 What Comes Next
Prompt engineering is evolving rapidly. More teams are building tools to manage and test prompts as part of the software development lifecycle.
Some important trends include:
- Growing use of tools like LangSmith and Flowise for prompt debugging
- A shift toward dynamic prompt generation, especially in agent-based systems
- Stronger defenses against adversarial prompts, such as input validation
- Testing across different models to ensure compatibility and quality
These changes suggest that prompting will soon feel more like product design than simple text formatting.
Final Thought
The performance of your AI system depends heavily on prompt quality.
That means writing with clear structure, not guesswork. It means testing with real examples, not assumptions. And it requires building in safety, not just adding polish.
When language becomes your logic, prompt engineering becomes system design.
Treat it with the same care.





Access slots and table games via casino mirror
Teknoloji Kıbrıs Teknoloji Kıbrıs, Kıbrıs teknoloji, teknolojikibris, elektronik eşyalar, Kıbrıs ucuz ev eşyası, teknolojik aksesuar kıbrıs
Awesome! Its genuinely remarkable post, I have got much clear idea regarding from this post
Hi i think that i saw you visited my web site thus i came to Return the favore I am attempting to find things to improve my web siteI suppose its ok to use some of your ideas
Somebody essentially help to make significantly articles Id state This is the first time I frequented your web page and up to now I surprised with the research you made to make this actual post incredible Fantastic job