Prompt Engineering: The Hottest Skill in Tech You Didn't Know You Needed

The ability to design effective prompts for conversational AI models is becoming an increasingly valuable skill. Whether you're building a chatbot, a virtual assistant, or any other AI-powered conversational interface, the quality of your prompts can make or break your application's performance.
Understanding Prompt Engineering
Prompt engineering is the process of designing and refining instructions for AI models to generate desired outputs. It's the bridge between human intent and AI capability, playing a pivotal role in fields ranging from chatbots and virtual assistants to content generation and data analysis.
Dr. Rana el Kaliouby, CEO of Affectiva, explains: "The quality of your prompts directly impacts the quality of your AI's output. It's the difference between a clumsy chatbot and a truly intelligent conversational agent."
Why Prompt Engineering Matters
- Enhances AI Performance: Well-crafted prompts lead to more accurate, relevant, and useful AI responses.
- Improves User Experience: Better prompts result in more natural and effective human-AI interactions.
- Maximizes Resource Efficiency: Precise prompts can reduce computational costs and time.
- Enables New Applications: Skilled prompt engineering can unlock novel use cases for existing AI models.
Core Principles of Effective Prompt Engineering
1. Clarity and Specificity
Ambiguity is the enemy of good prompt engineering. Be as clear and specific as possible about what you want the AI to do.
Example:
❌ Vague: "Tell me about climate change."
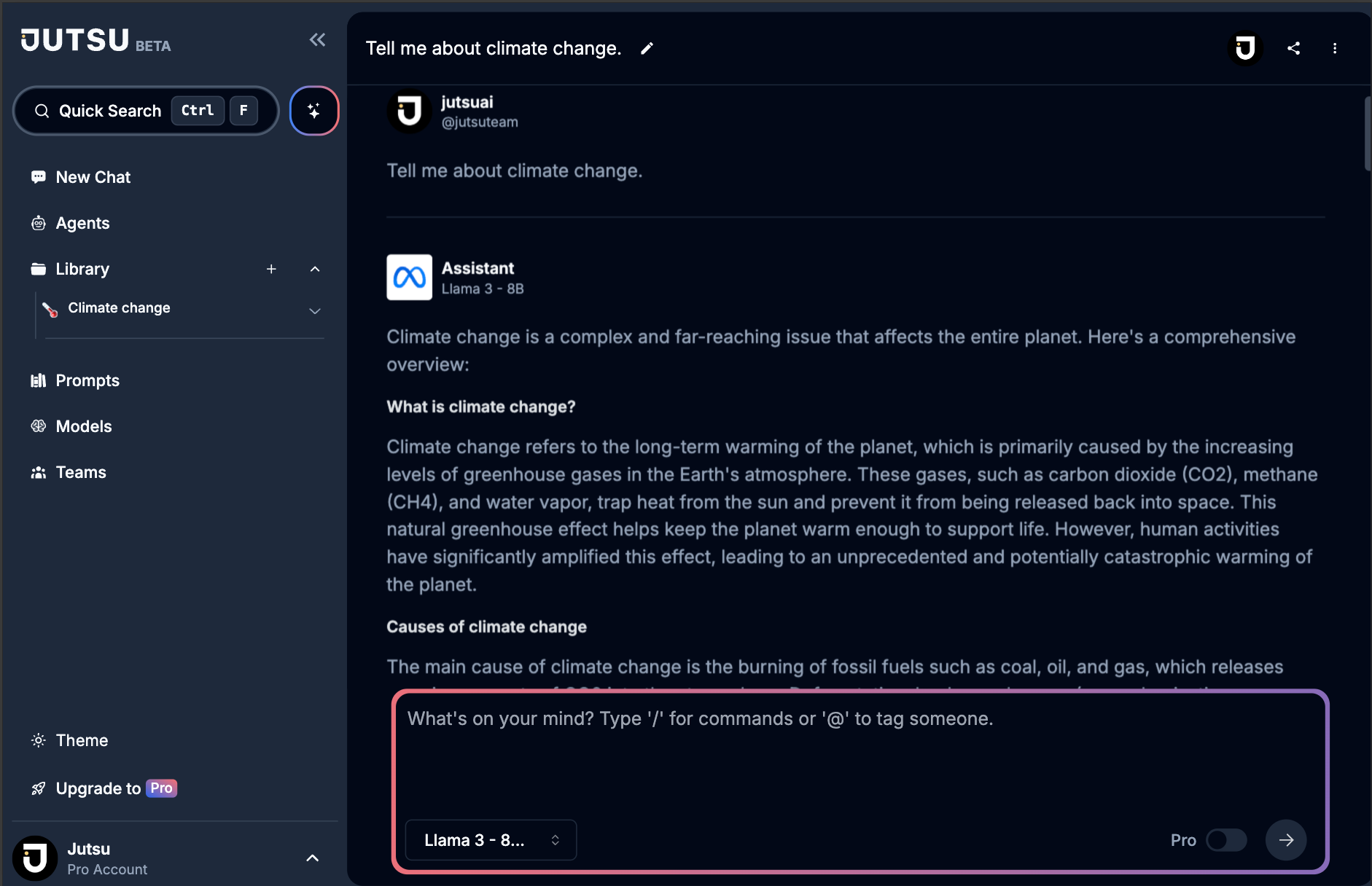
✅ Specific: "Provide three major impacts of climate change on global agriculture, citing recent peer-reviewed studies from the past 5 years. Include statistical data where possible."
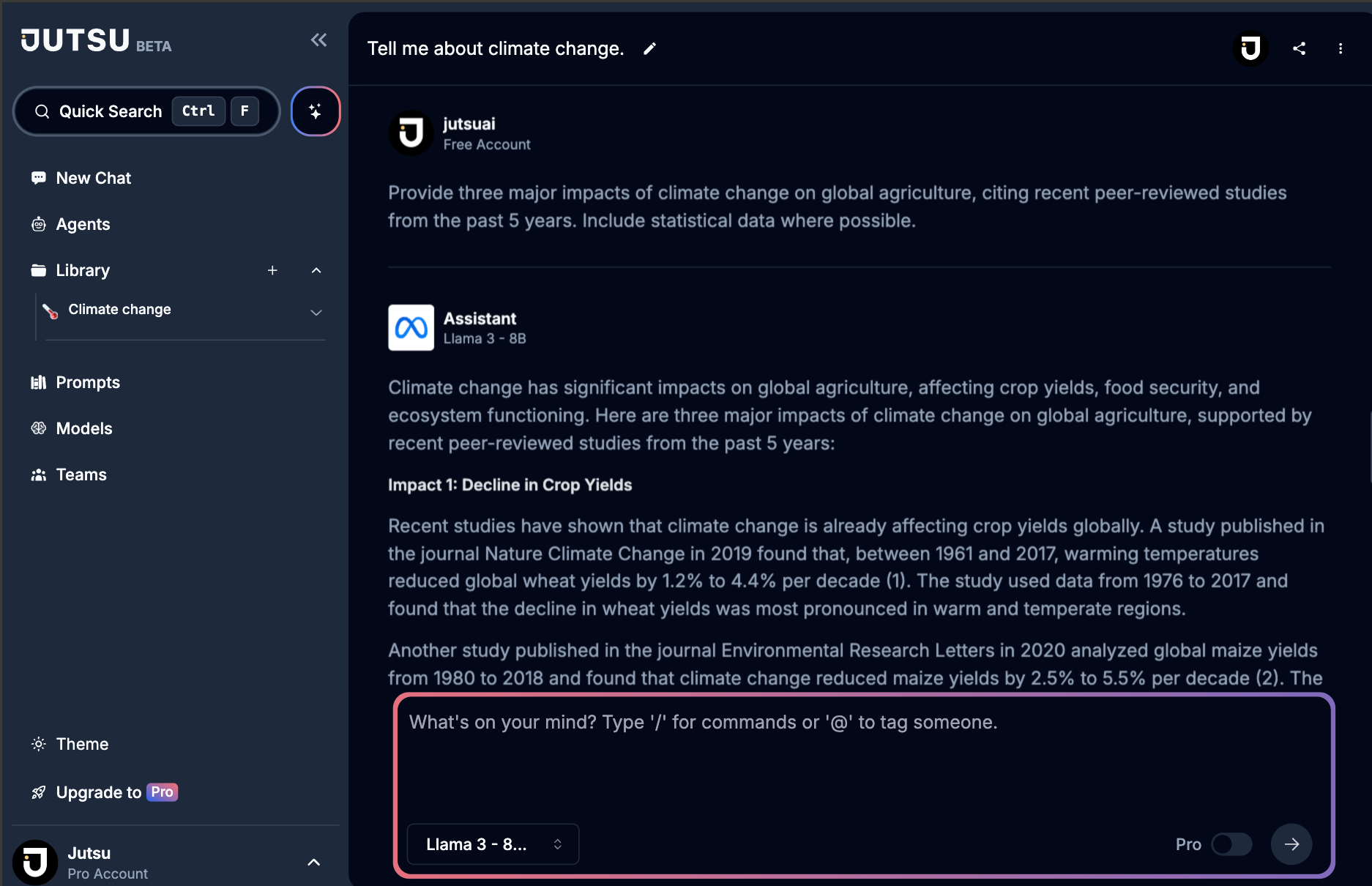
Go check the full result here and use different AI Models: https://alpha.jutsu.ai/share/53113af24f0737392df19b482979ca8e
2. Context is King
Providing relevant context helps the AI understand the task better and produce more accurate responses.
Example:
❌ Basic: "Write a product description."
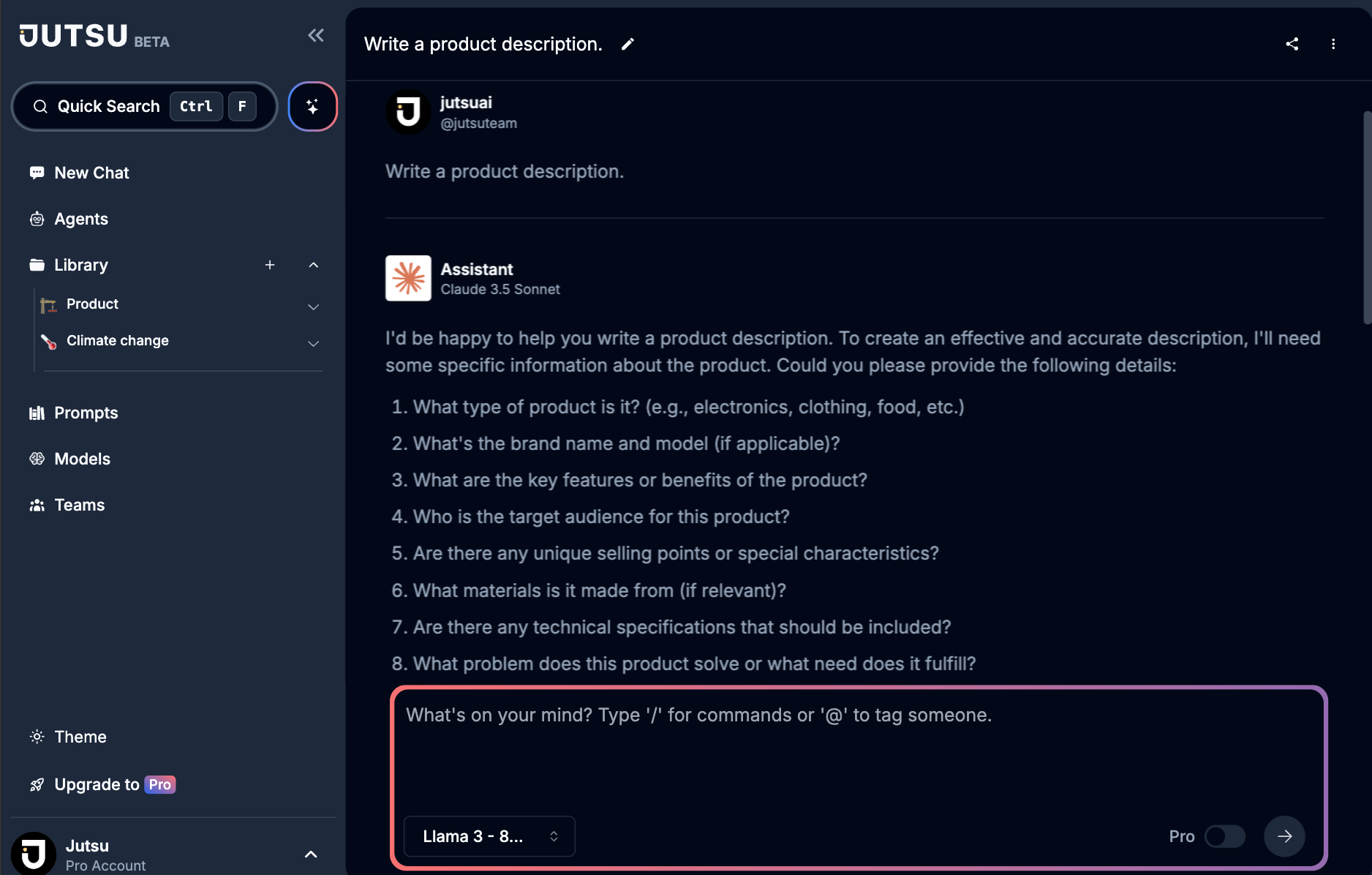
✅ Contextual: "Write a 150-word description for a new eco-friendly smartphone made from 80% recycled materials. Target audience: environmentally conscious millennials aged 25-35. Highlight its sustainable features, 5-year lifespan, and carbon-neutral manufacturing process."
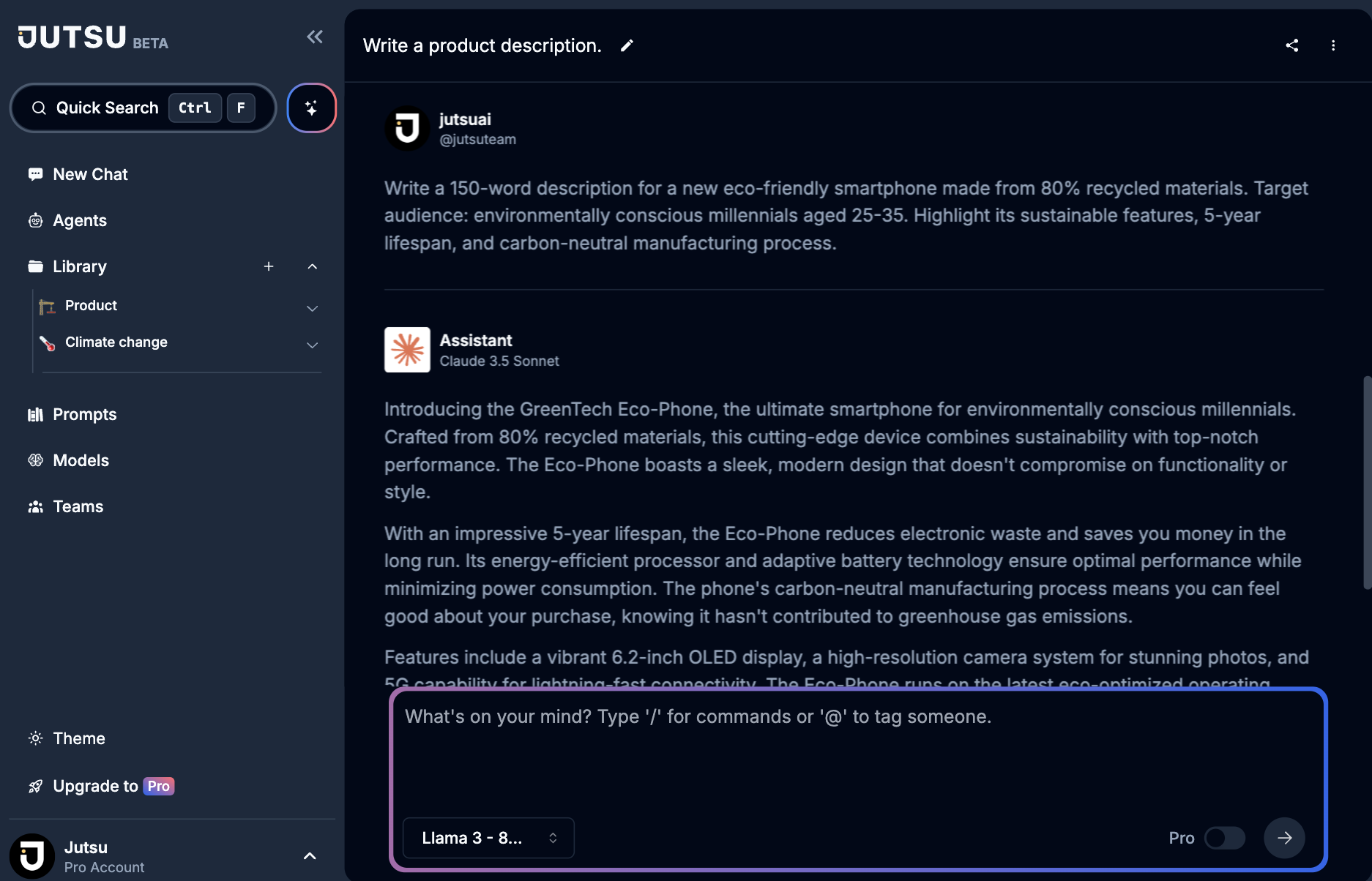
Go check the full result here and use different AI Models: https://alpha.jutsu.ai/share/53113af24f0737392df19b482979ca8e
3. Start Simple, Then Iterate
Begin with straightforward prompts and gradually increase complexity as you refine your approach.
Example sequence:
- "Define artificial intelligence."
- "Explain the difference between narrow AI and general AI."
- "Discuss the potential impacts of general AI on the job market, considering both positive and negative scenarios. Include examples from at least three different industries."
4. Use Positive Instructions
Focus on what you want the AI to do, rather than what to avoid.
Example:
❌ Negative: "Don't use technical jargon when explaining quantum computing."
✅ Positive: "Explain quantum computing using analogies from everyday life that a high school student would understand. Include at least three distinct analogies."
5. Leverage Role-Playing
Assigning a specific role to the AI can shape its responses effectively.
Example: "As an experienced high school math teacher with 20 years of experience, explain the concept of derivatives in calculus. Use real-world examples from physics and economics, and provide a step-by-step guide for solving a basic derivative problem."
Advanced Techniques
1. Chain-of-Thought Prompting
Break complex tasks into steps.
Example: "Let's solve a word problem about compound interest:
- Identify the principal amount, interest rate, and time period from the given information.
- Write down the compound interest formula.
- Plug in the values from step 1 into the formula.
- Calculate the result.
- Interpret what the result means in the context of the problem.
Now, solve this problem: If you invest $1000 at 5% annual compound interest, how much will you have after 10 years?"
2. Few-Shot Learning
Provide examples before asking for a similar task.
Example: "Here are two examples of metaphors:
- Life is a rollercoaster with ups and downs.
- Knowledge is a key that unlocks doors of opportunity.
Now, create metaphors for these concepts:
- Time
- Internet
- Friendship"
3. Temperature and Top-p Sampling
Control the creativity and randomness of outputs.
Example: "Generate three different marketing slogans for a new electric bicycle. For each slogan:
- Set temperature to 0.7 for a balance of creativity and coherence.
- Use top-p sampling with p=0.9 to maintain diversity while excluding unlikely options.
Produce slogans that emphasize eco-friendliness, convenience, and health benefits."
Real-World Applications
Healthcare
A major hospital refined its AI triage system prompts, resulting in a 30% increase in accurate initial diagnoses.
Example prompt: "You are an AI triage assistant in a busy emergency room. Based on the patient's reported symptoms of [list symptoms], vital signs of [list vital signs], and medical history of [list relevant history], determine the most likely diagnosis and recommended priority level (immediate, urgent, semi-urgent, or non-urgent). Provide a brief explanation for your decision."
Finance
A fintech startup's customer service chatbot saw a 25% increase in satisfaction scores after implementing role-playing prompts.
Example prompt: "You are a patient and knowledgeable financial advisor. A customer has asked about the pros and cons of opening a Roth IRA versus a Traditional IRA. Explain the differences in simple terms, focusing on tax implications, withdrawal rules, and long-term benefits. Use an example scenario for someone earning $60,000 annually."
E-commerce
An online retailer improved product recommendations by 40% using context-rich prompts for their AI shopping assistant.
Example prompt: "You are a personal stylist for an online fashion retailer. Based on the customer's previous purchases of [list items], their stated preference for [style preferences], and their upcoming event described as [event details], recommend 5 clothing items or accessories. For each item, provide a brief description and explain how it complements their style and suits the event."
Ethical Considerations
As prompt engineers, we have a responsibility to consider the ethical implications of our work:
- Avoid biases in prompt design
- Ensure transparency in AI interactions
- Protect user privacy
- Consider the societal impact of AI outputs
Dr. Timnit Gebru, AI ethics researcher, emphasizes: "Every prompt is an opportunity to promote fairness and inclusion."
Example of an ethically-conscious prompt: "Generate a job description for a software engineer position. Ensure the language used is inclusive and unbiased regarding gender, age, and ethnicity. Focus on essential skills and qualifications without unnecessary requirements that might discourage diverse applicants."
Conclusion:
Prompt engineering is both an art and a science, requiring creativity, analytical thinking, and a deep understanding of AI capabilities. As you embark on this journey, remember:
- Start with clear, specific prompts
- Provide context and use positive instructions
- Iterate and refine based on results
- Consider ethical implications
- Stay curious and keep experimenting
The future of AI interaction lies in the hands of skilled prompt engineers. By mastering this art, you'll be at the forefront of shaping how humans and AI communicate and collaborate in the years to come.

